Tagged with
digital manufacturing
Latest Posts
How Creaform Met the Need for Enhanced Accuracy, Versatility, and Efficiency of voestalpine Stahl GmbH
High-precision measurements, shorter surveying times and the rapid further processing of the data obtained convinced voestalpine Stahl.
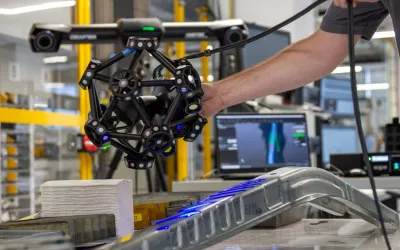
SFM improves its client reporting and the quality control of its transformer tanks through 3D scanning
Latvian company SFM, a provider of transformer tanks, has been using Creaform MetraSCAN BLACK 3D scanner with VXelements software for 2 years, to provide high-quality 3D measurement reports for its products.
When you get a piece of sheet metal, it tends to be soft and weak, and can be bent easily—comparing with the metal blocks. But if it is so weak, why product developers are still applying the sheet metal to the auto parts, or design it into enclosure, housing, bracket and much more? The fact is that the sheet metal parts can be strengthened accordingly, so that they can play their roles in different applications. In this article, we talk about some of the ways you can bolster the sheet metal parts.
Electroforming is an additive manufacturing process specialized for the production of high precision metal parts. Its uniqueness is that you can grow metal parts atom by atom, providing extreme accuracy and high aspect ratios. Typical precision of a electroformed part goes down to 1 to 2 μm, which is beyond what most other manufacturing technologies can reach.
Siemens Gamesa was looking for a 3D scanning system to take exact, agile measurements of wind turbines and their components so that they could be analyzed and processed using CAD software. The main goal was to dispense with traditional and inaccurate measuring tools such as tape measures and gauges, in favor of a more agile and precise method.
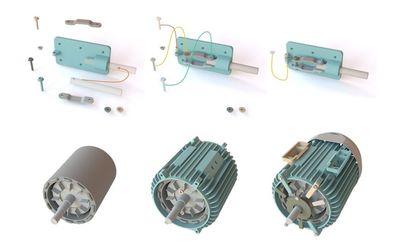
The manufacturing industry (largely) welcomed artificial intelligence with open arms. Less of the dull, dirty, and dangerous? Say no more. Planning for mechanical assemblies still requires more than scratching out some sketches, of course — it’s a complex conundrum that means dealing with arbitrary 3D shapes and highly constrained motion required for real-world assemblies.
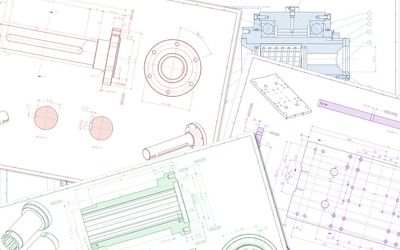
This blog post aims to guide you through the basic concepts and definitions of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T); more precisely, this includes what GD&T is, how it works, and why it is important to implement GD&T processes. Furthermore, it emphasizes that all of the geometric characteristics and tolerances written on a technical drawing are there for a specific purpose of functionality.